Fourteen New Transact-SQL Functions and One Improved
Applies to: SQL Server 2012.
SQL Server 2012 brings fourteen new T-SQL functions and improved another one.
Conversion Functions.
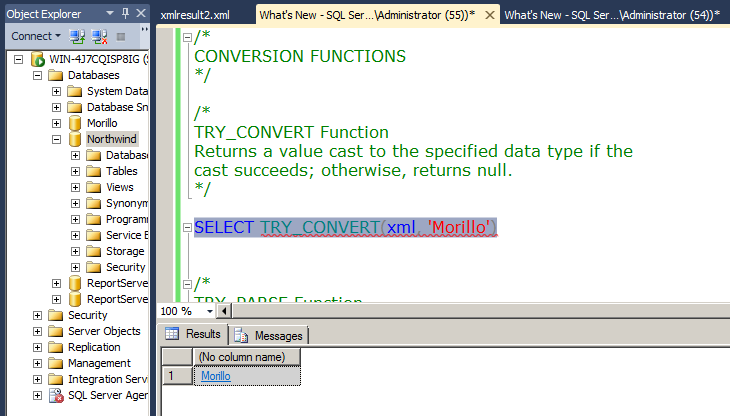
TRY_CONVERT Function. Returns a value cast to the specified data type if
the cast succeeds; otherwise, returns null.
TRY_PARSE Function. Returns the result of an expression, translated to
the requested data type, or null if the cast fails. Syntax:
TRY_PARSE(string_value AS data_type [USING culture]).
Example:
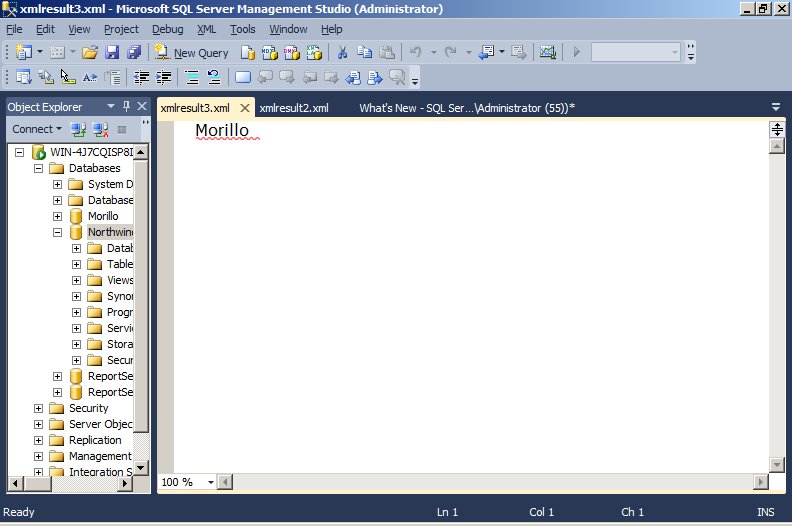
SELECT CASE WHEN TRY_PARSE('Morillo' AS decimal) IS NULL
THEN 'True'
ELSE 'False'
END
AS Result
Result:
True
(1 row(s) affected)
Example:
SELECT TRY_PARSE('1234.5' AS decimal(5,1)) AS Result
Result:
Result
---------------------------------------
1234.5
(1 row(s) affected)
PARSE Function. Returns the result of an expression, translated to the
requested data type. Syntax: PARSE (string_value AS data_type [USING culture])
Example:
SELECT PARSE('Monday, 13 december 2010' AS datetime2) AS Resultado
Result:
Resultado
----------------------
2010-12-13 00:00:00.00
(1 row(s) affected)
Date and Time Functions.
EOMONTH Function. This function returns the last day of the month that
contains the specified date, with an optional offset.
Example:
SELECT EOMONTH('2/2/2011')
Result:
----------------------
2011-02-28 00:00:00.00
(1 row(s) affected)
TIMEFROMPARTS Function. Returns a time value for the specified time and
with the
specified precision. Syntax: TIMEFROMPARTS(hour, minute, seconds, fractions,
precision)
Example:
DECLARE @time time
SET @time = TIMEFROMPARTS(23, 59, 59, 0, 0)
SELECT @time
Result:
----------------
23:59:59.0000000
(1 row(s) affected)
SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS Function. Returns a smalldatetime value for the
specified date and time. Syntax: SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS (year, month, day, hour,
minute)
Example:
SELECT SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS(2011, 10, 24, 16, 35)
Result:
-----------------------
2011-10-24 16:35:00
(1 row(s) affected)
DATEFROMPARTS Function. Returns a data value for the specified year,
month, and day. Syntax: DATEFROMPARTS (year, month, day)
Example:
SELECT DATEFROMPARTS(2011, 10, 24)
Result:
----------
2011-10-24
(1 row(s) affected)
DATETIMEFROMPARTS Function. Returns a datetime value for the specified
date and time. Syntax: DATETIMEFROMPARTS (year, month, day, hour, minute,
seconds, milliseconds)
Example:
SELECT DATETIMEFROMPARTS (2011, 10, 24, 16, 45, 43, 22)
Result:
-----------------------
2011-10-24 16:45:43.023
(1 row(s) affected)
DATETIME2FROMPARTS Function. Returns a datetime2 value for the specified
date and time
and with the specified precision. Syntax: DATETIME2FROMPARTS (year, month, day,
hour, minute, seconds, fractions, precision)
Example:
SELECT DATETIME2FROMPARTS(2011, 10, 24, 16, 45, 43, 22, 3) -- 3=Millisecods
-- 7=Nanoseconds
Result:
----------------------
2011-10-24 16:45:43.02
(1 row(s) affected)
DATETIMEOFFSETFROMPARTS Function. Returns a datetimeoffset value for the
specified date and time and
with the specified offsets and precision. Syntax: DATETIMEOFFSETFROMPARTS (year,
month, day, minute, seconds, fractions, hour_offset, minute_offset, precision).
Example:
SELECT DATETIMEOFFSETFROMPARTS(2011, 10, 24, 16, 45, 43, 0, 12, 0, 3)
Result:
----------------------------------
2011-10-24 16:45:43.000 +12:00
(1 row(s) affected)
Logical Functions.
CHOOSE Function. Returns the item at the specified index from a list of
values. Syntax: CHOOSE (index, val1, val2[, val_n]).
Example:
SELECT CHOOSE( 1, 2.30, 2.90, 4.10) as 'Discount Price'
Result:
Discount Price
---------------------------------------
2.30
(1 row(s) affected)
IIF Function. Returns one of two values, depending on whether the boolean
expression evaluates to true or false. Syntax: IIF (boolean_expression,
true_value, false_value).
Example:
DECLARE @value1 int=1
DECLARE @value2 int=5
SELECT IIF(@value1 > @value2, 'True', 'False').
Result:
-----
False
(1 row(s) affected)
Mathematical Functions.
LOG Function. Returns the natural logarithm of the specified float
expression. Syntax
LOG (float_expression[, base]).
By default returns the natural logarithm, with base e, where e=2.718281828
Example:
SELECT LOG(10)
Result:
----------------------
2.30258509299405
(1 row(s) affected)
Example:
SELECT LOG(10,10)
Result:
----------------------
1
(1 row(s) affected)
String Functions.
CONCAT function. Returns a string that is the result of concatenating two or
more string values.
Examples:
SELECT 'Alberto' + ', ' + 'Morillo'
SELECT CONCAT('Alberto', ' ', 'Morillo', ' ', 'Rodriguez')
Results:
----------------
Alberto, Morillo
(1 row(s) affected)
-------------------------
Alberto Morillo Rodriguez
(1 row(s) affected)
FORMAT function. Returns a value formatted with the specified format and
optional culture. Syntax: FORMAT (value, format[, culture]).
DECLARE @d DATETIME = '10/24/2011';
--SELECT FORMAT (@d, 'd', 'es-es') AS Result; -- Spanish - Spain
--SELECT FORMAT (@d, 'd', 'es-DO') AS Result; -- Spanish - Dominican Republic
--SELECT FORMAT (@d, 'd', 'af') AS Result; -- Afrikaans
SELECT FORMAT (@d, 'd', 'hy') AS Result; -- Armenian
Where to get the list of cultures?
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.globalization.cultureinfo(VS.80).aspx
SELECT FORMAT(47.127, '0.00') as Price
SELECT FORMAT(47.127, '$0.00', 'es-DO') as Price
![[Company Logo Image]](images/SQLCofee.jpg)
