Contained Databases in SQL Server 2012
Applies to: Microsoft SQL Server 2012.
Contained databases are a new feature in SQL Server 2012 and are defined on MSDN
Library as ”a database that is isolated from other databases and from the
instance of SQL Server that hosts the database”.
The containment setting of a database can be NONE, PARTIAL or FULL. But only
NONE and PARTIAL are supported on SQL Server 2012.
Benefits and characteristics.
The following are some of the benefits and characteristics that contained
databases have:
 They make easier to migrate databases from one server to another. Errors related
to orphan users are no longer an issue with contained databases, since a
contained database user can now be created without an associated login.
They make easier to migrate databases from one server to another. Errors related
to orphan users are no longer an issue with contained databases, since a
contained database user can now be created without an associated login.
 Authentication can now occur at the database level.
Authentication can now occur at the database level.
 Contained database users can be Windows and SQL Server authentication users.
Contained database users can be Windows and SQL Server authentication users.
 A contained database user can access only contained database objects. They
cannot access system databases and cannot access server objects.
A contained database user can access only contained database objects. They
cannot access system databases and cannot access server objects.
 Metadata is stored on the contained database and not stored on system databases.
This makes contained databases more portable than the databases we know.
Metadata is stored on the contained database and not stored on system databases.
This makes contained databases more portable than the databases we know.
Disadvantages and limitations.
Some disadvantages and limitations are the following:
 There are some security concerns. A database owner can create contained database
users without the permission of a DBA. The possibility of denial of service
attacks exist with contained databases using AUTO_CLOSE option. For security
best practices about contained databases, please see the references shown at the
end of the article.
There are some security concerns. A database owner can create contained database
users without the permission of a DBA. The possibility of denial of service
attacks exist with contained databases using AUTO_CLOSE option. For security
best practices about contained databases, please see the references shown at the
end of the article.
 Partially contained databases cannot use replication, change data capture,
change tracking, numbered procedures, schema-bound objects that depend on
built-in functions with collation changes. You may find more limitations on the
references shown at the end of this article.
Partially contained databases cannot use replication, change data capture,
change tracking, numbered procedures, schema-bound objects that depend on
built-in functions with collation changes. You may find more limitations on the
references shown at the end of this article.
Requirements of contained databases.
 It is required to enable contained databases on the instance.
It is required to enable contained databases on the instance.
 The contained database needs to be added to the connection string or specified
when connecting via SQL Server Management Studio.
The contained database needs to be added to the connection string or specified
when connecting via SQL Server Management Studio.
Step-by-step instructions on how to create a contained database.
To be able to create contained databases on a SQL Server 2012 instance, we need
to enable the contained database authentication option on the instance.
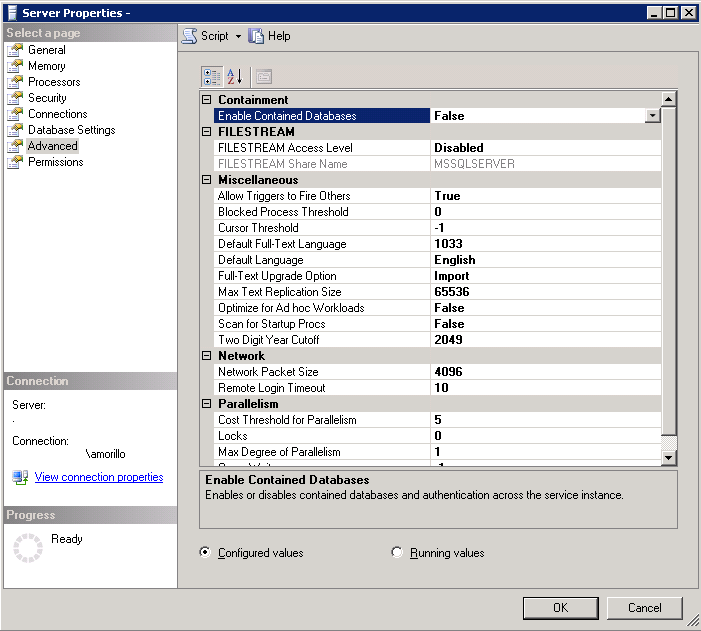
Open SQL Server 2012 Management Studio, connect to the instance, make a right
click on the name of the instance on Object Explorer, select the Advanced page
on the "Select a page" panel, and set to true the "Enable Contained Databases"
option.
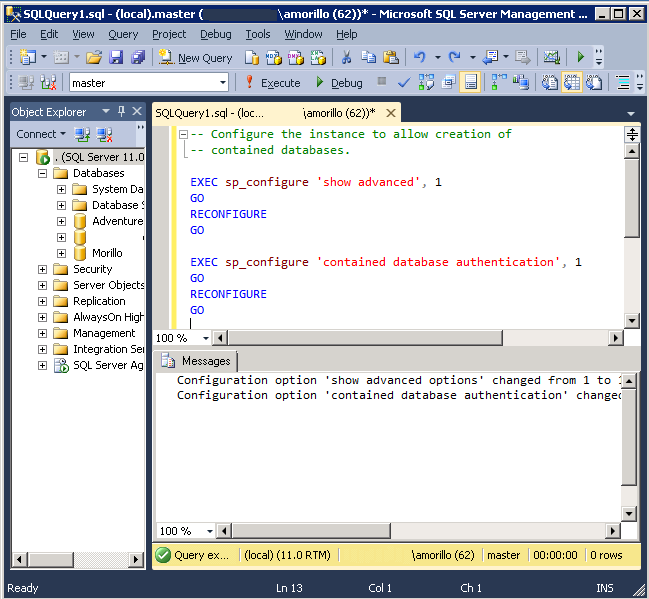
Alternatively, you can use sp_configure system stored procedure to enable
contained databases on the instance, as shown below.
EXEC
sp_configure
'show advanced',
1
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
EXEC
sp_configure
'contained database authentication',
1
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
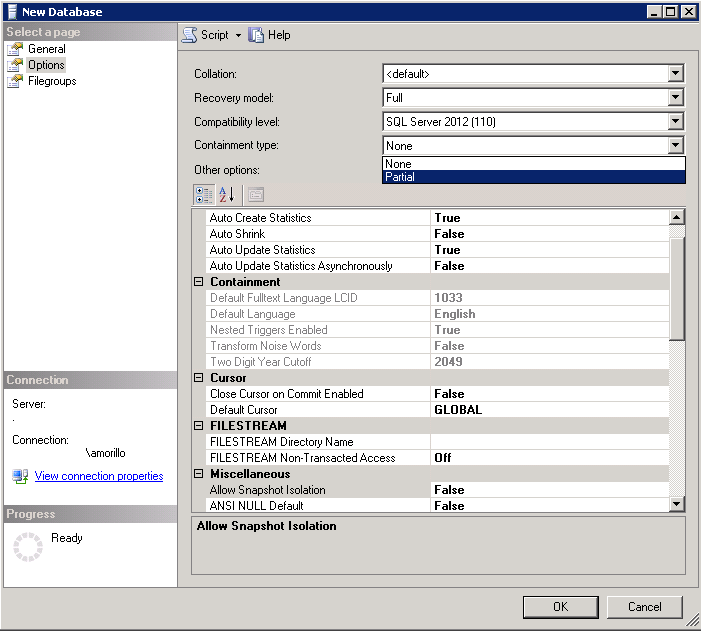
When a database is created the "Containment type" should be set to "partial" to
make the database a contained database, as shown below.
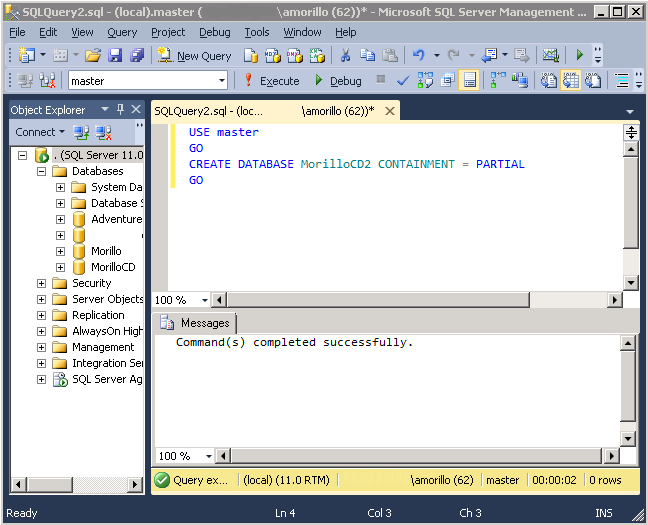
This can be done using T-SQL too, as shown below.
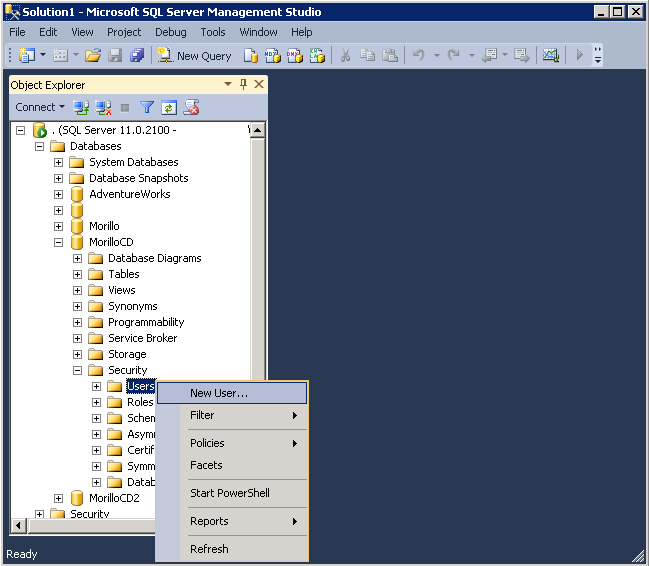
A contained database allows the creation of a database user that is not
associated to an instance login. A contained database user can be created
expanding the Security folder on the contained database, making a right click on
the Users folder and selecting the "New User" option.
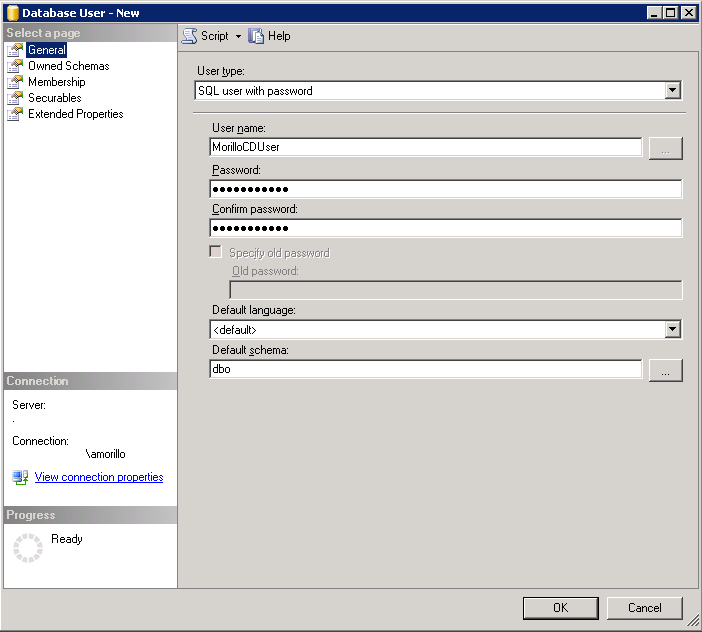
Next, set the user type to "SQL user with password", assign a user name, set the
password for the database user and specify the default schema for the user.
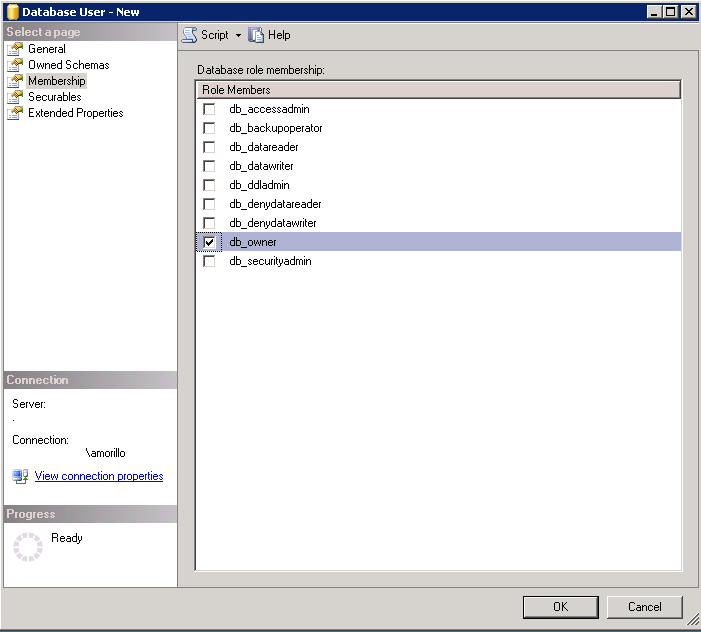
Specify the roles for this user on the database and click OK.
If you would like to create the contained database user using T-SQL, please see
the example below.
CREATE
USER
[MorilloCD2User]
WITH
PASSWORD=N'p@ssw0rd123',
DEFAULT_SCHEMA=[dbo]
GO
![[Company Logo Image]](images/SQLCofee.jpg)
